-
Промышленная зона Иньчжуан, уезд Мэнцюнь, город Цанчжоу, провинция Хэбэй, Китай
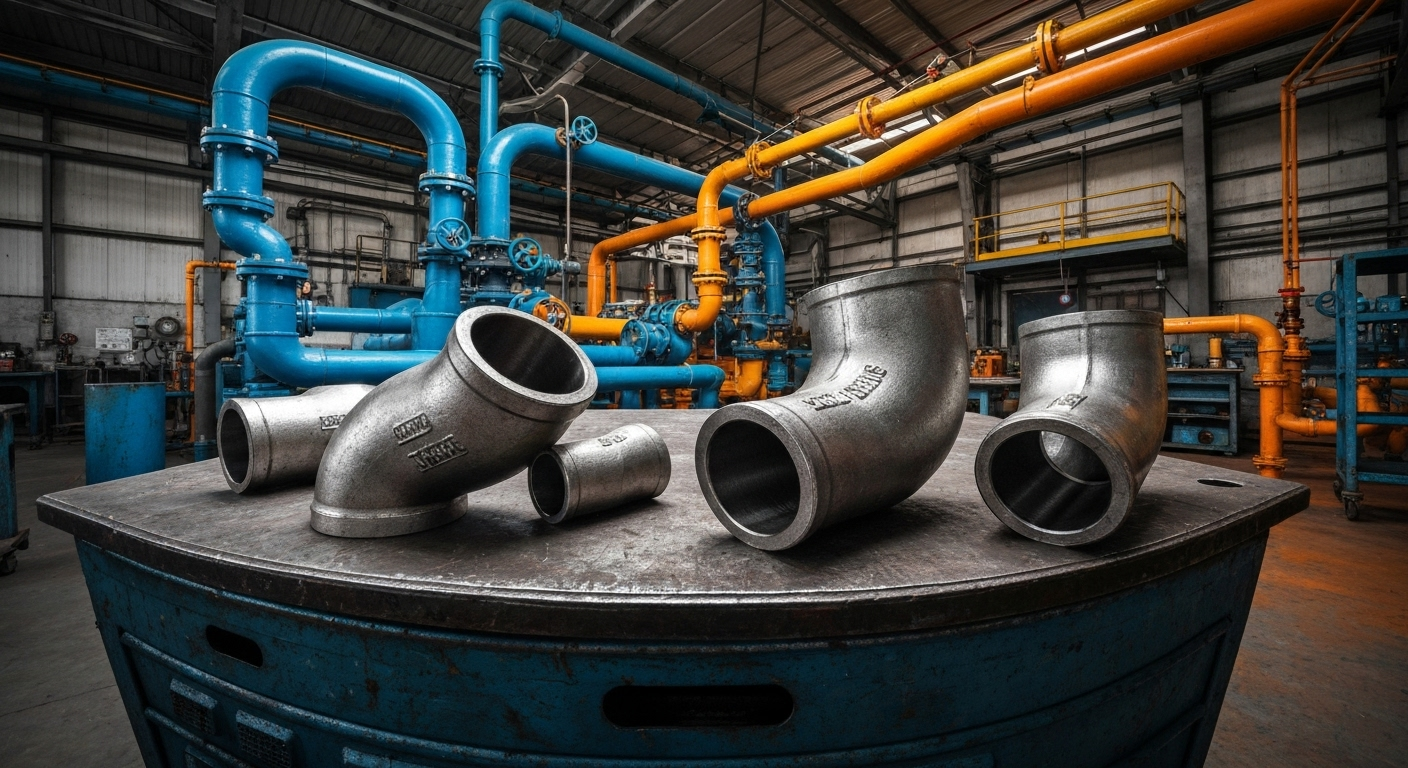

ASTM A234 WPB Elbow: Основное руководство по сварным фитингам

Основные моменты
Here’s a quick look at what you’ll learn about ASTM A234 WPB elbows:
- ASTM A234 WPB is a standard specification for carbon steel pipe fittings suitable for moderate to high-temperature service.
- These fittings, especially the carbon steel elbow, are essential for changing flow direction in various pipeline systems.
- You can find them in different angles, such as 45° and 90°, and radiuses, including long radius (LR) and short radius (SR).
- They are manufactured as either seamless or welded, with each type serving different pressure and application needs.
- Carbon steel offers excellent strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness compared to other materials.
Введение
When you’re working with pipeline systems, choosing the right components is critical for safety and efficiency. Among the most important parts are the pipe fittings that connect everything. An ASTM A234 WPB elbow is a key player in this field, especially for welded fittings. These components help you change the direction of a steel pipe run with reliability and strength. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about these essential fittings, from their specifications to their applications.
Understanding ASTM A234 WPB Elbows
A carbon steel elbow is a fitting used to change the direction of flow between two pipes. The designation ASTM A234 WPB tells you a lot about its quality and purpose. It’s a specific grade of carbon steel designed for welded fittings that can handle moderate and high temperatures, making it a reliable choice for industrial piping.
This standard specification ensures that the elbow you’re using meets specific requirements for strength and durability. Understanding what “WPB” means and why carbon steel is the material of choice will help you select the right components for your project.
What Is ASTM A234 WPB?
The term ASTM A234 WPB might seem technical, but it’s easy to break down. ASTM stands for the American Society for Testing and Materials, which sets technical standards for a wide range of products. The A234 part refers to the standard specification for wrought carbon and alloy steel fittings intended for pressure piping at moderate to elevated temperatures.
The “WPB” part provides more detail. “W” means “wrought,” indicating the fitting is made by forging or forming rather than casting. “P” signifies “pressure,” confirming its suitability for pressure-containing systems. Finally, “B” corresponds to “Grade B,” which refers to the minimum yield strength of the raw material, aligning it with common pipe grades like ASTM A106 Grade B.
This standard ensures that the steel fittings you use are manufactured from fully killed steel and meet strict chemical and mechanical property requirements. This guarantees consistent performance and safety in demanding applications. You can find more details about this standard on the ASTM International website. [1]
Role of Carbon Steel in Welded Fittings
Carbon steel is a go-to material for welded fittings for several good reasons. Its primary components are iron and carbon, which gives it a fantastic combination of strength and hardness. While it has lower plasticity than some other metals, its toughness makes it perfect for systems that need to withstand significant stress.
When it comes to welded fittings, the properties of carbon steel are a major advantage. It is highly weldable, allowing for strong and durable connections that are essential in high-pressure or high-temperature environments. This makes installation and pipeline repair more straightforward and reliable.
Whether you are connecting a new steel pipe or modifying an existing layout, carbon steel elbows provide the structural integrity needed. Their ability to be manufactured with a specific wall thickness ensures they match the connected pipes perfectly, creating a seamless and robust system.
Types and Specifications of Carbon Steel Elbows
Not all carbon steel elbow pipe fittings are the same. They come in various types and specifications to suit different pipeline needs. The most common distinctions are the angle of the bend and the radius of the curve. You’ll typically encounter 45-degree and 90-degree elbows, which handle different directional changes.
Additionally, elbows are designed with either a long radius (LR) or a short radius (SR). This choice affects the flow characteristics and the amount of space the fitting occupies. Let’s explore these differences to help you understand which type is right for your application.
45 Degree vs. 90 Degree Elbows: Key Differences
The most common elbow angles you’ll work with are 90 degrees and 45 degrees. A 90-degree elbow, sometimes called a “vertical elbow,” creates a sharp, right-angle turn. It’s the most widely used type because it fits well with steel structures and building layouts.
A 45-degree elbow, on the other hand, provides a gentler change in direction. This seemingly small difference has a significant impact on the fluid dynamics within the pipe. Because the turn is less abrupt, a 45-degree elbow produces less frictional resistance and a lower pressure drop compared to a 90-degree elbow of the same nominal size.
Вот краткое сравнение:
- Angle of Turn: A 90-degree elbow makes a right-angle turn, while a 45-degree elbow makes a half-right-angle turn.
- Friction and Pressure: The 45-degree elbow causes less friction and pressure drop.
- Common Usage: The 90-degree elbow is the most common due to its suitability for structural layouts.
- Применение: 90-degree elbows are for sharp turns; 45-degree elbows are for slight directional adjustments.
Long Radius vs. Short Radius Designs
Besides the angle, the radius of the pipe elbow is another critical specification. The radius refers to the curvature of the bend. You can choose between a long radius (LR) and a short radius (SR) design, and yes, both are available for carbon steel elbows.
A long radius elbow has a curve radius that is 1.5 times the pipe’s nominal diameter (R = 1.5D). This creates a smoother, more gradual turn. In contrast, a short radius elbow has a radius equal to the pipe’s nominal diameter (R = 1.0D), resulting in a much sharper and more compact bend.
The choice between them depends on your system’s requirements for flow efficiency and space. LR elbows are preferred for maintaining flow rate and minimizing pressure drop, while SR elbows are ideal for tight spaces where a compact fitting is necessary.
Характеристика | Long Radius (LR) Elbow | Short Radius (SR) Elbow |
|---|---|---|
Radius | 1.5 x Pipe Diameter (1.5D) | 1.0 x Pipe Diameter (1.0D) |
Flow | Smoother flow, less turbulence, lower pressure drop | Sharper turn, more turbulence, higher pressure drop |
Приложение | High-pressure, high-flow-rate pipelines | Low-pressure systems or where space is limited |
Космос | Requires more space | Compact, ideal for tight installations |
Seamless vs. Welded Carbon Steel Elbows
When selecting a steel pipe elbow, you’ll also need to decide between seamless and welded construction. This refers to how the elbow was manufactured from its raw material. A seamless pipe elbow is made from a solid piece of seamless pipe, while a welded elbow is fabricated from a steel plate or a welded pipe.
Each manufacturing method has its own set of advantages and is suited for different applications. The primary difference lies in their structural integrity and how they are formed, which in turn influences their performance under pressure. Let’s look at how they are made and when to use each type.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
The manufacturing process for seamless and welded elbows is quite different. To make a seamless elbow, a piece of seamless pipe is heated and then pushed through a mold, or mandrel, which forces it into the shape of an elbow. Since it’s made from a single piece of steel pipe, there are no seams or joints.
Welded fittings, on the other hand, can be made in a couple of ways. One method involves forming a polygonal shell from a steel plate and then welding the seams. Another approach is to use a fusion-welded pipe with added filler metal as the starting material, which is then formed into an elbow.
The key distinction is the presence of a weld seam. Seamless elbows lack this, which some engineers prefer for critical applications. Advances in welding technology, however, have made modern welded fittings extremely reliable, even for manufacturing large-diameter elbows.
When to Choose Seamless or Welded Options
Deciding between a seamless or welded elbow often comes down to the specific demands of your pipeline systems. Seamless elbows are traditionally favored for applications involving higher pressure and critical services because their uniform structure has no weld seams, which could be potential weak points.
However, welded fittings have become increasingly robust and are a practical choice for many situations. They are often more cost-effective, especially for larger diameter elbows. Modern manufacturing and quality control ensure that welded options perform reliably in a vast range of industrial applications.
Consider these points when making your choice:
- Pressure Requirements: For extremely high-pressure applications, seamless is often the preferred choice.
- Pipe Diameter: Welded elbows are commonly available in larger sizes that may be difficult or expensive to produce as seamless.
- Стоимость: Welded fittings are generally more economical than their seamless counterparts.
- Применение: Evaluate the criticality of the service. For less demanding systems, welded fittings are perfectly suitable.
Choosing the Right ASTM A234 WPB Elbow
Selecting the correct ASTM A234 WPB elbow is crucial for the integrity and performance of your piping system. You can’t just pick any elbow; you need to consider several factors to ensure it fits perfectly and functions as intended. The main considerations are the elbow’s size, radius, and wall thickness.
These parameters must match the pipes they are connecting to and the operational requirements of the system, such as pressure and flow rate. Making the right choice ensures a secure, leak-free connection and an efficient pipeline. Let’s break down how to select the right specifications for your needs.
Selecting Size, Radius, and Wall Thickness
Getting the specifications right is the most important step in choosing an elbow. The size, radius, and wall thickness must align with the rest of your piping system to ensure a proper fit and safe operation.
First, the nominal size of the elbow must match the diameter of the pipes you are connecting. Next, you’ll need to decide between a long radius (LR) or short radius (SR) design based on space and flow requirements. As discussed, LR elbows offer smoother flow, while SR elbows are for tight corners. Finally, the wall thickness, often specified by a schedule number (e.g., SCH 40, SCH 80), must match the pipe’s wall thickness to handle the system’s internal pressure.
Here’s a checklist for selection:
- Nominal Size: Ensure the elbow’s diameter matches your pipe’s diameter.
- Radius: Choose a long radius for efficient flow or a short radius for compact spaces.
- Wall Thickness (Schedule): Select a schedule that matches your pipe’s thickness to handle the operating pressure.
- Angle: Determine if you need a 90°, 45°, or another angle for the directional change.
Application Scenarios for Butt-Weld Elbows
Butt-weld elbows are steel fittings designed to be welded directly to the end of a pipe. This connection method creates a strong, leak-proof, and continuous joint, making it the preferred choice for demanding applications. Unlike socket weld or threaded fittings, a butt-weld joint offers a smooth interior surface that minimizes pressure drop and turbulence.
Because of their robustness, butt-weld elbows are the standard for high-pressure and high-temperature services. You will commonly find them in critical pressure piping systems across various industries. For example, they are essential components in power plants for carrying steam, in chemical facilities for transporting aggressive fluids, and in oil and gas pipelines.
Their strength also makes them ideal for pipeline repair, as they can restore the full integrity of the pipe. While a socket weld fitting is suitable for smaller diameter pipes in less critical services, a butt-weld elbow is the superior choice when performance and safety are paramount.
Installation Guidelines for Welded Elbows
Proper installation is just as important as selecting the right part. When it comes to welded elbows, a correct installation process ensures a strong, lasting connection that maintains the integrity of your pipeline systems. The process involves careful preparation, precise welding, and thorough inspection.
Following a set of established guidelines for installing these steel fittings will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure a safe, leak-free joint. Let’s go over the key steps for preparation and welding, as well as the importance of post-installation quality checks.
Preparation and Welding Steps
A successful weld starts with good preparation. Before you begin welding, the ends of both the pipe and the elbow must be clean and properly beveled. This ensures that the filler metal can penetrate the joint completely, creating a strong bond. Any rust, oil, or contaminants must be removed.
During the welding process, it’s crucial to maintain proper alignment and a consistent gap between the parts. The choice of filler metal should be compatible with the carbon steel being joined. For systems with higher pressure, the quality of the weld is paramount. Unlike a socket weld elbow where the pipe is inserted, a butt-weld requires a precise, edge-to-edge connection.
Follow these key steps for installation:
- Clean and Bevel: Ensure the ends are clean and have the correct bevel angle.
- Align: Perfectly align the elbow and pipe to create a uniform gap.
- Tack Weld: Apply small tack welds to hold the fitting in place.
- Complete the Weld: Perform the main weld, ensuring full penetration and a smooth bead.
- Cooling: Allow the joint to cool properly, avoiding rapid cooling that could cause defects by bringing it below the critical range too quickly.
Контроль и обеспечение качества
Once the welding is complete, inspection and quality assurance are the final steps to guarantee a reliable joint. The first check is usually visual. You should inspect the weld for any visible defects like cracks, undercut, or lack of fusion. A smooth, uniform weld bead is a good sign of quality work.
For more critical applications, additional non-destructive testing (NDT) methods may be required. These can include radiographic (X-ray) or ultrasonic testing to check for internal defects that aren’t visible to the naked eye. It’s also important to measure the final dimensions to ensure they meet the project’s requirements.
In many industrial settings, a third-party inspection is performed to verify that the installation complies with the relevant standard specification, such as ASME B16.9. This provides an extra layer of quality assurance and confirms the pipeline is safe for operation. For more information on this standard, you can visit the ASME website. [2]
Advantages of ASTM A234 WPB Elbows
Choosing ASTM A234 WPB elbows for your project comes with a host of advantages. These fittings are known for their exceptional durability and performance, especially in systems that operate at higher pressure and temperature. Their robust construction ensures they can withstand significant mechanical stress without failing.
Compared to an alloy steel pipe or fittings made from other materials, carbon steel offers a unique balance of strength, cost-effectiveness, and reliability. Let’s delve into what makes their performance so dependable and why carbon steel is often the best material for the job.
Performance and Durability
The performance of ASTM A234 WPB elbows is defined by their strength and resilience. These fittings are engineered to manage the demands of industrial pipeline systems, including the ability to handle higher pressure and temperature fluctuations without compromising their structural integrity. This reliability is essential for maintaining safety and operational continuity.
Their durability translates to a long service lifetime. When properly installed and maintained, carbon steel elbows can last for decades, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing downtime. This long-term performance makes them a cost-effective investment for any large-scale project.
Whether you’re building a new pipeline or upgrading an existing one, you can count on the consistent performance of these fittings. Their ability to endure harsh conditions while maintaining a secure, leak-free connection is why they are a trusted component in so many industries.
Why Carbon Steel Over Other Materials?
While materials like stainless steel, nickel alloy, and other alloy steel options offer excellent corrosion resistance, carbon steel stands out for its unique combination of properties. For many applications, it provides the best overall value.
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its high strength and toughness at a much lower cost than stainless steel or nickel alloys. This makes it an economical choice for large-scale projects where material costs can add up quickly. It’s also highly versatile and easy to fabricate and weld.
Here’s why carbon steel is often preferred:
- Cost-Effectiveness: It offers impressive performance for a fraction of the cost of specialty alloys.
- Сила: Carbon steel has excellent tensile and yield strength, making it ideal for high-pressure applications.
- Temperature Resistance: It performs well in both moderate and elevated temperature services.
- Availability: Carbon steel fittings are widely available in a full range of sizes and specifications. While it may require coatings for corrosion protection in certain environments, its inherent strength and affordability make it the superior choice for a vast number of industrial applications.
Common Applications and Industry Uses
Thanks to their strength and reliability, ASTM A234 WPB elbows are used in a wide array of pipeline systems across numerous industries. You’ll find these essential components in everything from massive power plants and oil refineries to local water treatment facilities. Their versatility makes them a staple for many industrial projects.
They are particularly common in systems that transport fluids or gases under pressure, such as gas pipelines, chemical processing plants, and shipbuilding. Understanding the difference between industrial and plumbing applications can help you appreciate their broad utility.
Industrial vs. Plumbing Projects
The use of carbon steel elbows differs significantly between industrial and plumbing projects. In industrial settings, such as oil and gas pipelines or chemical plants, the focus is on handling high pressures, extreme temperatures, and potentially corrosive substances. Here, butt-weld carbon steel elbows are the standard due to their strength and leak-proof design.
Plumbing applications, like residential or commercial water supply, typically operate under much lower pressures. While carbon steel can be used, these systems might also employ other materials or connection types like threaded or socket weld fittings, which are easier to install and maintain for smaller-diameter pipes.
However, for larger-scale water treatment plants or municipal water mains, the durability of carbon steel fittings is often necessary. In these large-scale “plumbing” systems, the requirements begin to resemble those of industrial pipeline systems, making carbon steel an excellent choice.
Where to Source ASTM A234 WPB Elbows
Finding reliable suppliers for ASTM A234 WPB elbows is a key step for any project. You can source these fittings from specialized industrial piping suppliers, metal distributors, and manufacturers. Many suppliers operate online, allowing you to request quotes and place orders with delivery often promised within a few business days.
When choosing a supplier, it’s important to verify their credibility. Look for suppliers who can provide mill test certificates (MTCs) and documentation that proves the fittings meet the required standards. Reputable suppliers will have clear labeling on their products, including the grade, size, schedule, and heat number.
Here’s how to find the right source:
- Search Industrial Suppliers: Look for established distributors of pipe, valves, and fittings (PVF).
- Request Documentation: Always ask for MTCs and compliance certificates.
- Check for Quality Marks: Ensure products are clearly marked with all necessary information.
- Consider Third-Party Inspection: For critical projects, you may want to arrange a third-party inspection before shipment.
Заключение
In summary, understanding ASTM A234 WPB elbows is crucial for anyone involved in the welding and piping industries. These fittings offer essential advantages, from durability to performance, making them a popular choice for various applications. By grasping the differences between seamless and welded options, as well as how to select the right size and specifications, you can ensure efficient and effective installations. Whether you’re working on industrial projects or plumbing systems, knowing where to source high-quality ASTM A234 WPB elbows will empower you to make informed decisions. If you have any questions or need assistance with your next project, feel free to reach out for support!
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Are ASTM A234 WPB elbows available in both long radius and short radius types?
Yes, ASTM A234 WPB elbows are available in both long radius (LR) and short radius (SR) designs. The standard specification covers both types, allowing you to choose a long radius pipe elbow for smoother flow or a short radius one for installations in tight, compact spaces.
How do I determine the correct size elbow for my piping system?
To determine the correct size elbow, you must match its nominal size and wall thickness (schedule) to the steel pipe in your piping system. Both the elbow and the pipe must have the same diameter and schedule number to ensure a proper fit and to safely handle the system’s pressure.
What are the key benefits of butt-weld elbows in piping installations?
The key benefits of a butt-weld elbow include creating a strong, leak-proof joint that is as strong as the pipe itself. These welded fittings are ideal for pipeline systems with higher pressure and temperature, offering excellent durability and a smooth inner surface that minimizes flow restrictions.
Citations: [1] ASTM A234/A234M-23, Standard Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Moderate and High Temperature Service, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2023, www.astm.org/a0234_a0234m-23.html [2] ASME B16.9, Factory-Made Wrought Buttwelding Fittings, The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, NY, www.asme.org/codes-standards/find-codes-standards/b16-9-factory-made-wrought-buttwelding-fittings