-
Zone industrielle de Yinzhuang, comté de Mengcun, ville de Cangzhou, province de Hebei, Chine
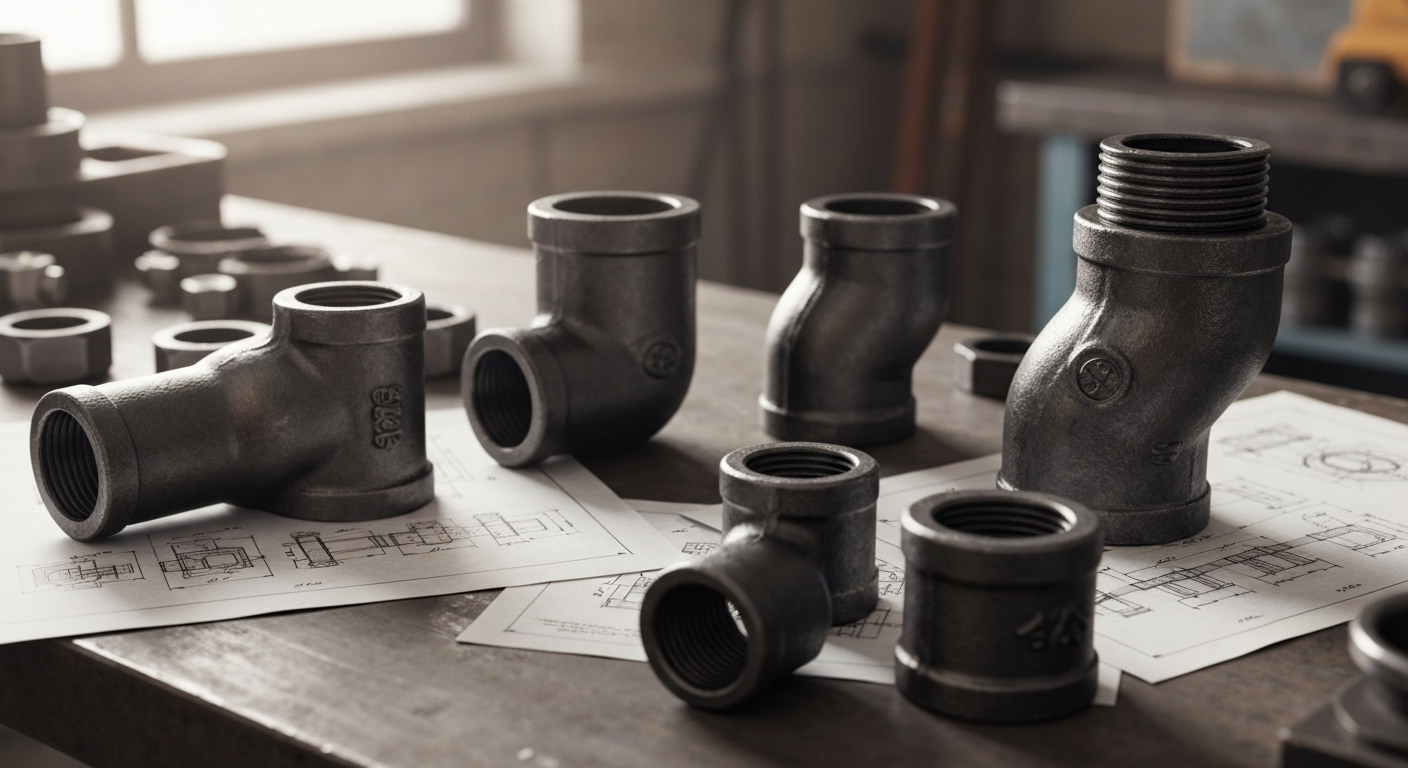

Raccords de tuyauterie ASTM A234 WPB : Applications dans diverses industries

Faits marquants
Here are the main takeaways from our guide on ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings:
- ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings are a standard for carbon and alloy steel fittings used in pressure pipelines.
- These fittings are essential for industrial applications that involve moderate and high temperatures.
- The specific chemical composition of WPB grade ensures excellent weldability and strength.
- They are available in various types, including elbows, tees, and reducers, for diverse system needs.
- Manufacturing follows strict quality standards to guarantee reliability and durability.
Introduction
Welcome to your complete guide on ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings! If you work with pipeline systems, you know how crucial the right components are. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) sets the standards for many materials, and their specifications for steel fittings are vital for safety and performance. These components are the backbone of countless industrial applications, from power plants to petrochemical facilities. This article will walk you through everything you need to know about these versatile and reliable fittings.
Overview of ASTM A234 WPB Pipe Fittings
So, what exactly does ASTM A234 cover? This is a standard specification for wrought carbon steel and alloy steel pipe fittings designed for moderate and high-temperature services. ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings are among the most common types used in pressure pipelines and pressure vessel fabrication.
This standard includes both seamless and welded construction types. Essentially, these fittings help change fluid direction, adjust flow rates, or connect pipes in a system. The “WPB” designation refers to a specific grade of weldable, pressure-rated carbon steel known for its strength and reliability.
Standard Specifications and Material Composition
The performance of these fittings comes down to their specific chemical composition. The ASTM A234 standard carefully outlines the material requirements to ensure consistent quality and safety. The Grade B (WPB) material is a carbon steel, but the standard also covers various alloy steel grades.
The carefully controlled carbon content is key to the material’s excellent weldability. For WPB grade, the maximum carbon is 0.30% in most product analyses, which provides a great balance of strength and flexibility. The table below outlines the primary chemical requirements for ASTM A234 WPB.
Élément | Composition, % |
|---|---|
Carbon (C) | 0.30 max |
Manganese (Mn) | 0.29-1.06 |
Phosphorus (P) | 0.050 max |
Sulfur (S) | 0.058 max |
Silicon (Si) | 0.10 min |
Chrome (Cr) | 0.40 max |
Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.15 max |
Types and Configurations Available
One of the major advantages of ASTM A234 fittings is the wide variety of types and configurations available. This versatility allows you to build complex piping systems tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re working with carbon steel or alloy steel fittings, you can find the right component for the job.
These fittings are designed to serve different functions within a pipeline, from changing direction to branching off. The most common types you’ll encounter include:
- Coudes : Used to change the direction of flow, typically at 45 or 90 degrees.
- Tees : Shaped like the letter “T,” a tee allows for a 90-degree branch from the main pipe run.
- Réducteurs : Used to connect pipes of different diameters, available as concentric or eccentric.
- Casquettes : Designed to seal the end of a pipe.
Beyond these basic types, you can also find crosses, nipples, and couplings. While most fittings are butt-welded, some configurations like socket weld or threaded fittings are also available under associated standards.
Manufacturing and Quality Standards
The manufacturing of ASTM A234 WPB fittings is a highly controlled process to ensure they meet stringent quality and safety standards. The process involves operations like forging, pressing, bending, and fusion welding to shape the raw material into the final fitting. Adherence to standards from organizations like ASME and ANSI is mandatory.
A critical part of the process is heat treatment, which enhances the mechanical properties and relieves internal stresses created during forming. This ensures the fittings can withstand the demanding conditions found in pressure vessel fabrication and high-pressure pipelines. Let’s look closer at the production and testing methods.
Production Processes: Seamless vs. Welded
ASTM A234 covers both seamless and welded pipe fittings, and the primary difference lies in the raw material used for their production. Understanding this distinction can help you select the right type for your application’s durability requirements.
A key part of manufacturing is the cooling process. After being formed at a high temperature, the fittings must be cooled at a controlled rate to prevent defects. The cooling rate should not be faster than cooling in still air to ensure the material’s integrity. Here’s a simple breakdown of the two types:
- Seamless Fittings: These are made from seamless steel pipes or tubes. The absence of a weld seam provides uniform strength and structure, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- Welded Fittings: These are manufactured from welded steel pipes or plates. Modern fusion welding techniques ensure that the weld seam is strong and reliable for most industrial uses.
Testing, Inspection, and Certification
To guarantee that every fitting meets the required specifications, a rigorous testing and inspection process is essential. This quality control step is what provides the certification that fittings are safe for their intended use. The main goal is to identify and eliminate any injurious defects that could compromise performance.
Manufacturers perform a series of tests to verify mechanical properties and structural integrity. These tests ensure the fitting’s wall thickness, tensile strength, and minimum yield strength all meet or exceed the standard’s requirements without surpassing any specified maximum limits. Common inspection procedures include:
- Hardness Test: Ensures the material is not too brittle or soft.
- Tensile Test: Measures the fitting’s strength and ductility.
- Hydrostatic Test: Checks for leaks under pressure.
- Visual and Dimensional Inspection: Confirms the fitting is free from surface defects and meets all dimensional tolerances.
Industrial Applications of ASTM A234 WPB Pipe Fittings
The reliability and strength of ASTM A234 WPB carbon steel fittings make them a top choice for a vast range of industrial applications. Their primary use is in pressure piping systems where fluids or gases are transported at moderate to high temperatures and pressures. You can find them in everything from gas pipelines to complex chemical processing facilities.
These fittings are the connecting components that allow long, complex pipeline networks to function safely and efficiently. Industries like energy generation, particularly in power plants, rely heavily on these parts for their steam and water lines. The following section will explore some of these key sectors in more detail.
Usage Across Oil & Gas, Power, and Petrochemical Sectors
The robust nature of ASTM A234 WPB fittings makes them indispensable in several major industries that operate under demanding conditions. Their ability to handle high-temperature services and high-pressure flows is critical for safety and operational efficiency in these sectors.
From upstream extraction to downstream refining, these sectors depend on reliable pressure pipelines to transport materials. Do you work in any of these fields? You’ve likely seen these fittings in action. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Pétrole et gaz : Used in pipelines for transporting crude oil, natural gas, and other hydrocarbons from extraction sites to refineries and distribution centers.
- Power Plants: Essential for boiler systems, steam lines, and cooling water circuits in fossil fuel, nuclear, and other power generation facilities.
- Industrie pétrochimique : Employed in process piping for transporting chemicals, solvents, and other raw materials used in manufacturing plastics, fertilizers, and more.
Guidelines for Proper Selection, Sizing, and Maintenance
Selecting the right ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings involves understanding their application and the specific requirements of your project. Pay close attention to the chemical composition and minimum yield strength, ensuring compatibility with the equipment they’ll connect to. Sizing is equally important; consider the wall thickness and overall durability of the fittings. Regular maintenance is key for longevity—inspect for injurious defects and ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent issues in high-temperature services. Always reference the latest revision of ASME for guidelines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings play a crucial role across multiple industries, notably in oil and gas, power generation, and petrochemicals. Their standardized specifications and versatile configurations ensure that they meet the rigorous demands of various applications. By understanding manufacturing processes and quality standards, industries can select the right fittings to enhance operational efficiency and safety. Regular maintenance and proper sizing further contribute to their longevity and performance. If you’re looking to implement ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings in your projects or need guidance on selection and maintenance, feel free to reach out for a consultation. Your success in utilizing these fittings starts with the right information!
Questions fréquemment posées
What are the main benefits of using ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings?
The primary benefits are their excellent durability, high tensile strength, and exceptional weldability, which simplifies fabrication. They are designed to perform reliably in pressure piping systems, especially in applications that operate at temperatures outside the material’s critical range, ensuring long-term safety and performance in demanding environments.
How do you differentiate between seamless and welded ASTM A234 WPB fittings?
The main difference is the manufacturing origin. Seamless fittings are made from seamless pipe, resulting in a uniform structure and wall thickness with no weld joints. Welded fittings are produced from welded pipe or plate, with the manufacturing process ensuring the fusion weld is free from injurious defects.
How should ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings be maintained in industrial settings?
Proper maintenance involves regular visual inspections for corrosion, erosion, or mechanical damage, particularly in industrial applications with elevated temperature. Ensure the fittings continue to operate under suitable conditions and are not subjected to improper cooling cycles that could cause stress. Replacement should occur if any significant degradation is found.