-
Yinzhuang Industrial zone,Mengcun county,Cangzhou city,Hebei province,China
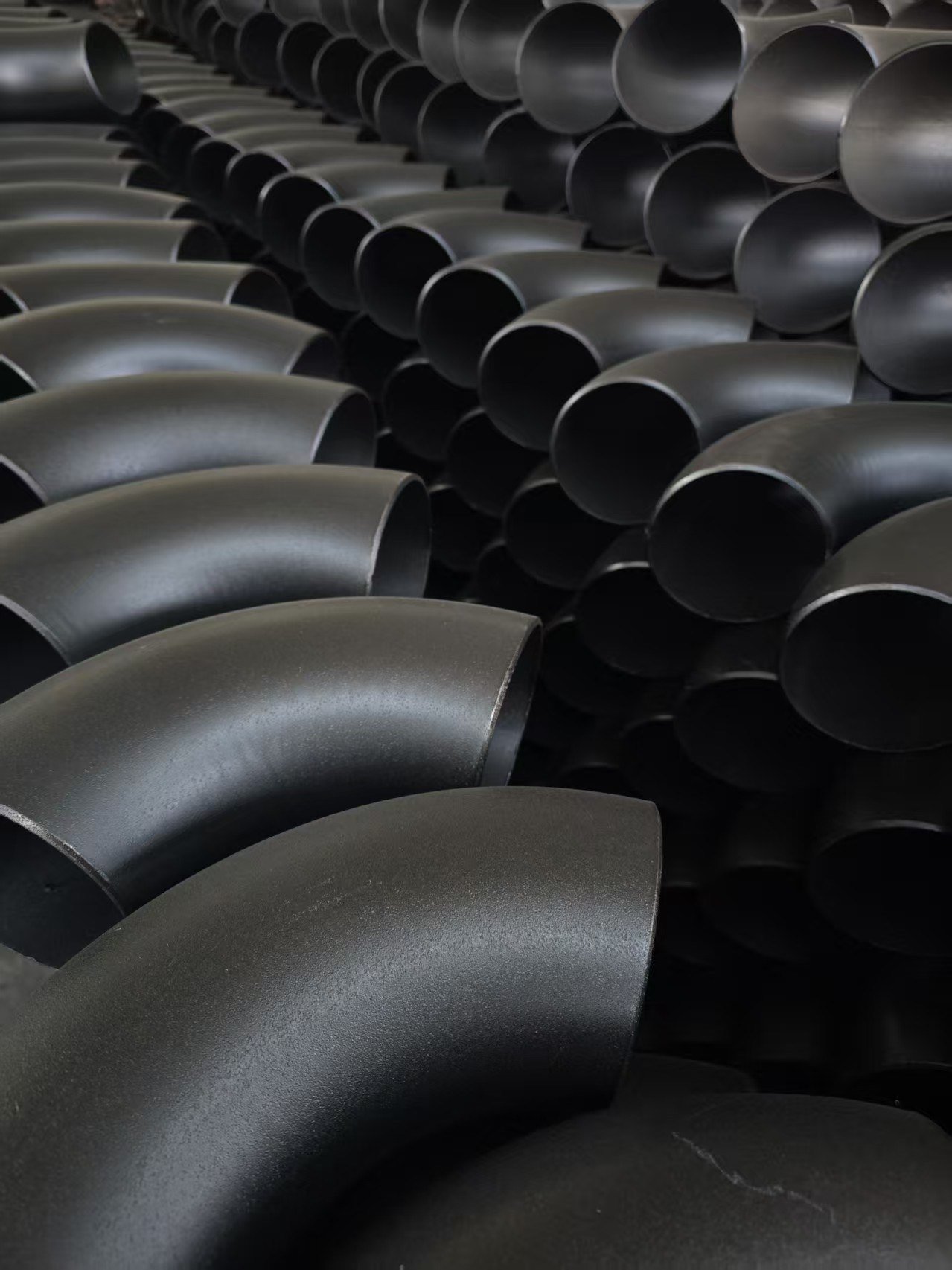

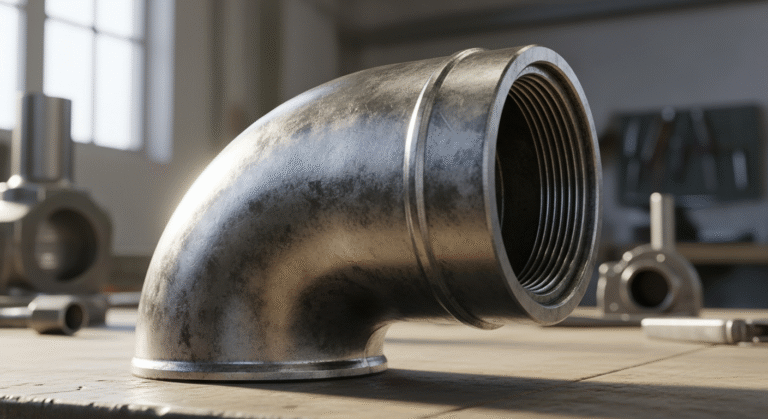
A234 GR WPB Elbow: Your Guide to Weld Fittings
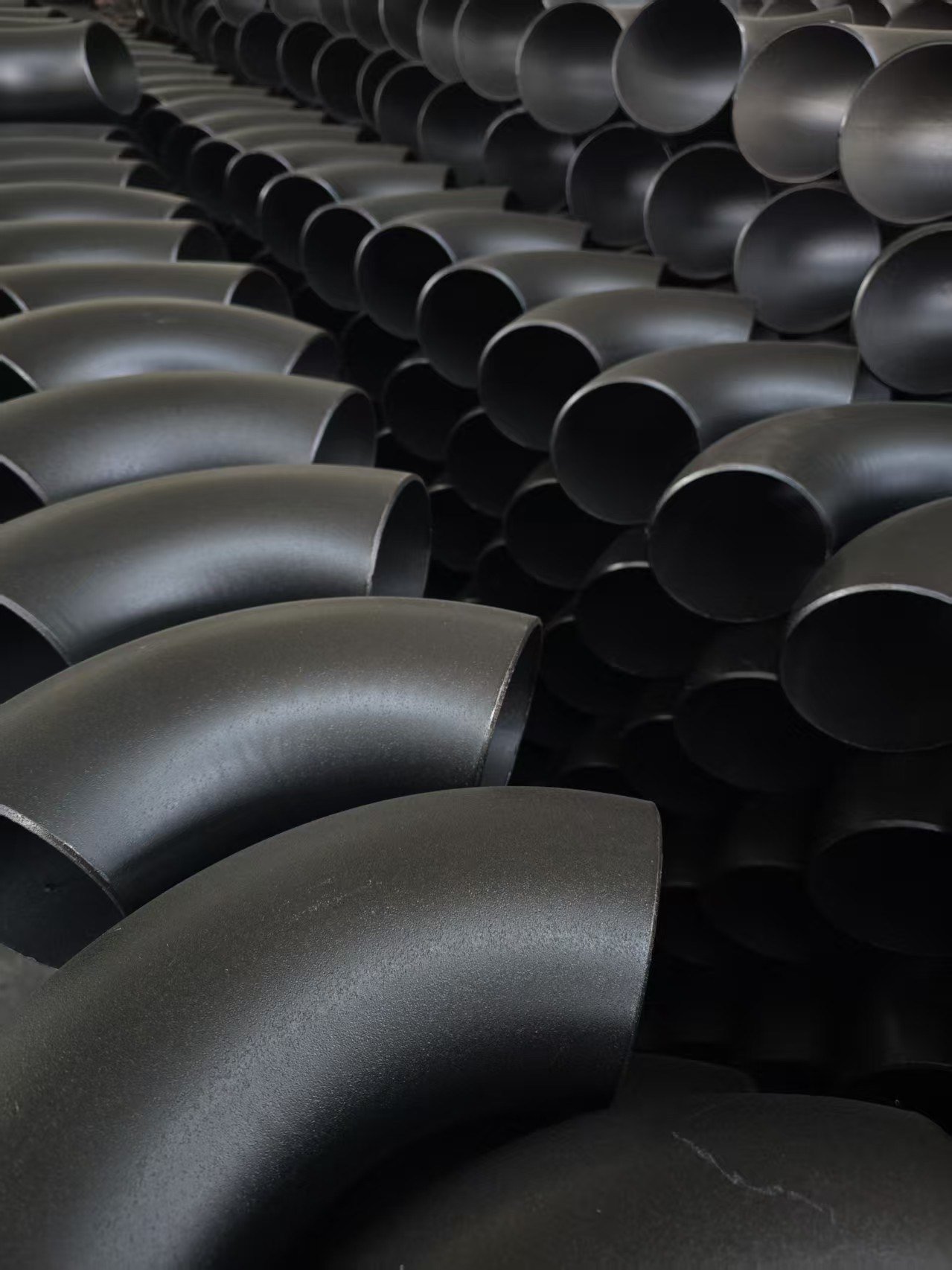

ASTM Grades of Alloy steel buttweld pipe fittings: What are they?
ASTM grades of alloy steel buttweld pipe fittings include various classifications, such as A234 WPB, which denotes the material’s specific chemical and mechanical properties. These grades ensure that fittings can withstand high pressure and temperature applications, making them essential in industries like oil and gas, power generation, and construction.
Key Highlights
- ASTM A234 Grade WPB is a standard specification for wrought carbon steel and alloy steel pipe fittings.
- These buttweld fittings are designed for moderate and high-temperature service in pressure piping systems.
- A steel elbow changes the direction of flow and is available in 45° and 90° angles.
- You can choose between long radius (LR) for smoother flow and short radius (SR) for tight spaces.
- They are manufactured from high-quality steel pipe and are used in industries like oil, gas, and petrochemicals.
Introduction
Welcome to your guide on A234 GR WPB elbows! If you’re involved in any project that uses piping, you’ve likely come across these essential components. A234 WPB is a standard specification for wrought carbon steel and alloy steel pipe fittings used in pressure piping. These steel fittings play a critical role in changing the direction of a steel pipe, ensuring your system operates efficiently and safely. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about these versatile pipe fittings.
Understanding A234 GR WPB Elbows
So, what does A234 GR WPB actually mean? Let’s break it down. ASTM A234 is the standard for wrought carbon steel and alloy steel pipe fittings. The “W” stands for “wrought,” meaning it’s formed rather than cast. “P” indicates it’s suitable for “pressure” applications, and “B” refers to Grade B, which specifies a minimum yield strength, similar to common steel pipe grades.
These WPB carbon steel components are primarily used as butt weld fittings. This means the steel elbow is welded directly to the pipe, creating a strong, leak-proof connection. Understanding this terminology is the first step to choosing the right steel fittings for your needs. Now, let’s explore the material properties and standards that make these elbows so reliable.
Material Composition and Properties
The performance of an A234 WPB elbow comes down to its specific material composition. The raw material for these fittings must be fully killed steel, which can include forgings, bars, plates, or seamless steel pipe. This ensures a uniform structure free of defects. The chemical makeup consists mainly of carbon steel, with controlled amounts of manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, and silicon.
This precise blend of elements gives the elbow its desirable mechanical properties. A key characteristic is its minimum yield strength, which ensures it can withstand significant pressure without deforming. According to the ASTM A234 standard, these fittings are designed to be strong and durable for moderate and high-temperature services.
The controlled composition, including a carbon content typically below 0.30%, also provides excellent weldability. This makes it easier to install them securely within a piping system. The thickness range available further allows you to match the elbow perfectly to your pipe’s specifications for consistent strength across the entire line.
Common Standards and Certifications
To ensure safety and reliability, A234 WPB elbows must conform to strict industry standards. The primary standard specification is ASTM A234, which covers the material, manufacturing, and testing requirements for wrought carbon and alloy steel fittings. For dimensions, these elbows almost always adhere to ASME B16.9, which standardizes the sizes and tolerances for buttwelding fittings. Source
Beyond these primary standards, other specifications like MSS-SP-75 may also apply, depending on the application. When you purchase these fittings, they should come with a Mill Test Certificate (MTC) or EN 10204-3.1 certificate. This document verifies the material’s chemical and mechanical properties, confirming it meets the required standards for Grade B steel.
For critical applications, such as in pressure vessel fabrication, you may also request a third-party inspection to provide an extra layer of quality assurance.
Standard | Description |
|---|---|
ASTM A234 | Covers material specifications for wrought steel pipe fittings. |
ASME B16.9 | Defines dimensions and tolerances for buttwelding fittings. |
MSS-SP-75 | Specification for high-test, wrought, buttwelding fittings. |
EN 10204 | Specifies types of inspection documents for metallic products. |
Types of A234 GR WPB Elbow Fittings
A234 WPB elbows come in several types to accommodate different piping layouts and flow requirements. The most common feature distinguishing these buttweld fittings is their bend radius and angle. You’ll primarily find them in long radius (LR) and short radius (SR) versions, which impacts how sharply the pipe turns.
Additionally, the steel elbow is available in different angles to facilitate various directional changes. The most standard options are the 90-degree elbow and the 45-degree elbow. Understanding these variations is key to designing an efficient and space-conscious piping system. Let’s look closer at the differences between radii and the available angles.
Long Radius vs. Short Radius Elbows
Choosing between a long radius (LR) and short radius (SR) steel elbow depends on your priorities for flow efficiency and space. A long radius elbow has a curve radius that is 1.5 times the pipe’s nominal diameter (R = 1.5D). This creates a gentler turn, which is ideal for maintaining flow rate and minimizing pressure drop.
On the other hand, a short radius elbow has a curve radius equal to the pipe’s nominal diameter (R = 1.0D), resulting in a much sharper change of direction. While SR elbows are perfect for tight or confined spaces, their abrupt turn can increase turbulence and friction inside the carbon steel pipe.
Here’s a quick comparison:
- Long Radius (LR): Smoother flow, less pressure drop, preferred for efficiency.
- Short Radius (SR): More compact, ideal for tight spaces, higher pressure drop.
- Application: LR elbows are the default choice unless space constraints demand an SR elbow.
Available Angles: 45°, 90°, and Custom Bends
The most common angles for A234 WPB elbows are 90° and 45°. A 90-degree elbow is used to make a sharp, right-angle turn in a piping system. It’s the most frequently used type for redirecting flow in a perpendicular direction. The 45-degree elbow provides a gentler turn, which is useful for slight directional adjustments and creating complex piping layouts.
These standard angles are readily available for various pipe sizes, from small diameters to large size fittings. The ends of these elbows are beveled to facilitate a clean butt weld connection to the pipe, ensuring a strong and seamless joint.
In addition to the standard 45° and 90° options, you can also find other angles for specific needs:
- 180° Elbows: Also known as “returns,” these are used to completely reverse the direction of flow.
- Custom Bends: For unique applications, manufacturers can produce elbows with custom angles (e.g., 30° or 60°) or larger bend radii (like 3D or 5D) to meet project requirements.
Sizing and Schedules for WPB Elbows
To ensure a perfect fit and maintain system integrity, A234 WPB elbows are defined by their size and schedule. The nominal size refers to the diameter of the pipe it connects to, while the schedule indicates the wall thickness. It’s crucial that the elbow’s size and schedule match the carbon steel pipe you are using.
A mismatched wall thickness can create weak points in the pipeline, compromising its ability to handle pressure. The wide thickness range available ensures you can find an elbow for nearly any standard pipe. Let’s examine the specific size and schedule options, as well as their impact on pressure ratings.
Range of Sizes and Wall Thickness Options
A234 WPB elbows are available in an extensive range of sizes to suit virtually any piping project. The nominal size can range from as small as 1/2 inch up to 80 inches or even larger for custom applications. This versatility makes them a staple in everything from small-scale systems to massive industrial pipelines.
Equally important is the wall thickness, which is specified by a schedule number. A higher schedule number means a thicker wall, making the fitting stronger and more suitable for high-pressure applications. The available thickness range is broad, ensuring compatibility with various pipe types.
Common schedule options include:
- Sch 20, Sch 40 (STD): Standard thicknesses for many applications.
- Sch 80 (XS): Extra-strong, for higher pressure systems.
- Sch 160, XXS: Double extra-strong, for extreme pressure and temperature conditions.
This wide selection of sizes and schedules ensures you can find the perfect steel pipe fitting for your specific needs.
Pressure Ratings and Temperature Limits
The pressure rating and temperature limits of an A234 WPB elbow are critical factors determined by its material and wall thickness. These fittings are specifically designed for moderate and high-temperature service in pressure piping systems. The maximum pressure an elbow can handle is directly related to its schedule—a thicker wall (higher schedule) translates to a higher pressure rating.
The material’s minimum yield strength is a core property defined by the ASTM A234 standard, ensuring the fitting can withstand internal pressure without failing. This makes these elbows a reliable choice for demanding environments, including pressure vessel fabrication.
When selecting an elbow, always consult the ASME B31 pressure piping codes to determine the appropriate schedule for your operating conditions. Factors to consider include:
- Maximum operating pressure.
- Operating temperature range.
- The fluid being transported.
- Any potential for pressure surges.
Applications in Piping Systems
Thanks to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, A234 WPB elbows are used across a vast array of industries. They are a fundamental component in any pressure piping system that requires a change in direction. You’ll find them connecting carbon steel pipe and alloy steel pipe in sectors where reliability is paramount.
The most common applications are in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, but their use extends far beyond that. From power plants to water treatment facilities, these fittings provide a dependable solution for managing fluid and gas flow. Next, we’ll explore their role in these specific industries.
Use in Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical Industries
In the oil, gas, and petrochemical sectors, reliability is non-negotiable. A234 WPB elbows are a go-to choice for these industries because they can safely handle the transport of volatile fluids and gases under high pressure and temperature. The raw material used to make these fittings ensures they can withstand corrosive environments often found in refineries and processing plants.
These elbows are used to construct the complex networks of pressure piping that move crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. They work seamlessly with other components like carbon steel flanges and valves to create robust and leak-free systems. Their durability minimizes maintenance needs and ensures operational safety in these critical infrastructures.
Key applications include:
- Crude oil and natural gas pipelines.
- Refinery processing units.
- Chemical manufacturing plants.
- Power plants that use fossil fuels.
Other Industrial and Commercial Uses
Beyond the energy sector, A234 WPB elbows have numerous other industrial and commercial uses. Their combination of strength and affordability makes them an excellent choice for a wide range of applications. In shipbuilding, for example, they are used in engine room piping, ballast systems, and other onboard fluid transport networks.
Water treatment plants and municipal water systems also rely on these carbon steel fittings for constructing durable and long-lasting pipelines. Their simple, welded installation and proven performance make them a practical steel pipe fitting for general industrial piping.
Other common uses include:
- HVAC systems in large commercial buildings.
- Fire protection sprinkler systems.
- Manufacturing facilities for various processes.
- General-purpose fluid and air transport.
Whether you need carbon steel fittings or alloy steel fittings, the A234 WPB grade offers a dependable solution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, A234 GR WPB elbows are essential components for various piping systems, particularly in industries like oil, gas, and petrochemicals. Their material composition, sizing options, and pressure ratings make them versatile and reliable for many applications. By understanding the different types of elbows available, including long and short radius fittings, you can make informed decisions that optimize your projects while ensuring safety and efficiency. Remember, selecting the right elbow is crucial for the integrity of your piping system. If you have any questions or need personalized guidance, feel free to reach out for a consultation to help you choose the best fittings for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I select the correct A234 GR WPB elbow for my project?
To select the right elbow, you must match it to your pipe. Consider the nominal size (diameter), wall thickness (schedule), and required angle (e.g., 45- or 90-degree elbow). Ensuring these three parameters align with your carbon steel pipeline is crucial for a secure and compatible fit in your pipe fittings system.
What welding methods are recommended for WPB elbows?
A234 WPB butt weld fittings are installed using fusion welding techniques like Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG). It is essential to follow the proper welding procedure and use a compatible filler metal as per the standard specification for carbon steel pipe to ensure a strong, reliable joint. Source
How do A234 GR WPB elbows compare to other carbon steel elbows?
A234 WPB elbows are superior to generic carbon steel elbows because they are manufactured to a specific ASTM standard. This guarantees their chemical composition and minimum yield strength, making them suitable for moderate to high-temperature pressure piping. Other generic pipe fittings may not offer this same level of verified performance and safety.