-
Yinzhuang Industrial zone,Mengcun county,Cangzhou city,Hebei province,China
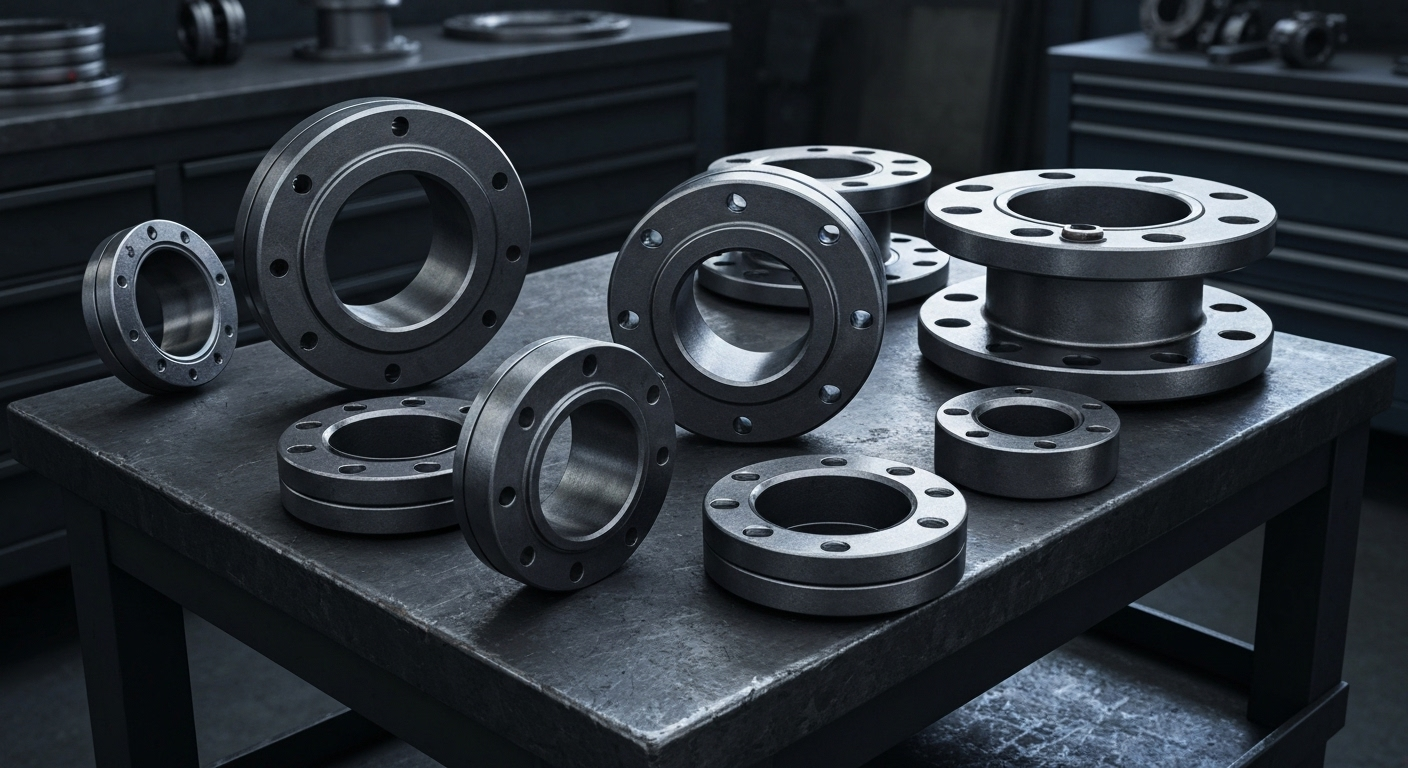

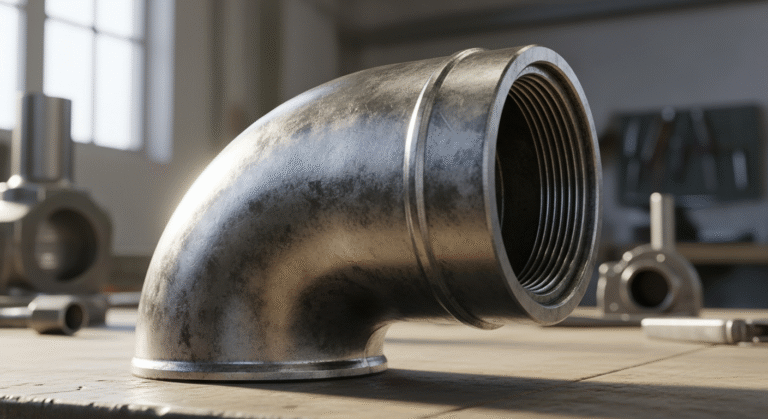
A105 Flange Types: Slip-On, Weld Neck, and More
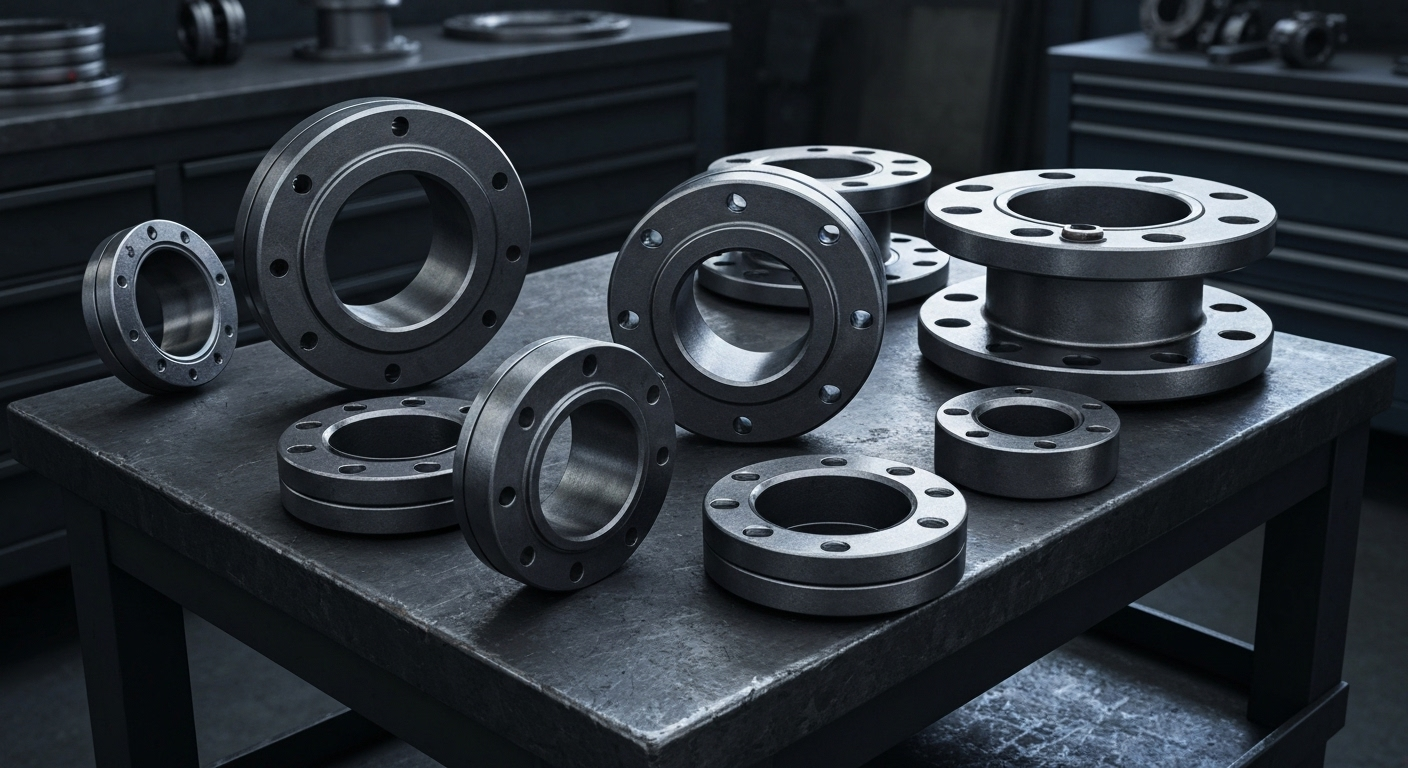

Key Highlights
- ASTM A105 flanges are a top choice for carbon steel pipe fittings used in ambient and high-temperature service. The primary types include the slip-on flange for low-pressure pipelines and the weld neck flange for high-stress applications.
You can buy A105 flanges from specialized industrial suppliers or distributors of pipeline fittings and carbon steel components. When purchasing, ensure the flange meets astm standards, matches your specific pipe size and pressure requirements, and comes from a reputable supplier experienced with weld neck flange and fittings for pipelines.
- The primary types include the slip-on flange for low-pressure pipelines and the weld neck flange for high-stress applications.
- A105 flanges offer excellent mechanical properties, durability, and cost-effectiveness compared to materials like stainless steel.
- Understanding the specification, including size, pressure class, and face type, is crucial for selecting the right flange.
- The manufacturing process, typically forging, ensures high strength and reliability for demanding industrial use.
- Weld neck flanges provide superior structural integrity by transferring stress from the flange to the pipe.
Introduction
Welcome to your guide on ASTM A105 flanges! If you work with industrial pipelines, you know how critical every component is. Flanges are essential pipe fittings that connect pipes, valves, and other equipment to form a complete piping system. Among the various materials available, A105 carbon steel is a popular and reliable choice known for its strength and versatility. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of A105 flanges, from slip-on to weld neck, to help you understand which is best for your needs.
Overview of ASTM A105 Flanges
So, what exactly is an ASTM A105 flange? It’s a flange manufactured from carbon steel according to the ASTM A105 specification. This standard covers forged carbon steel piping components for use in pressure systems at ambient and higher-temperature service. The specification ensures the flange has specific mechanical properties and chemical compositions, making it a reliable choice for various industrial applications.
The manufacturing process for these pipe fittings typically involves forging, which creates a strong, durable product. These flanges are commonly used in industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation to connect pipelines and equipment securely. Now, let’s look closer at their properties and common uses.
Key Properties and Chemical Composition
The reliability of an A105 flange comes down to its specific chemical composition and mechanical properties. As a type of carbon steel, it primarily consists of iron, with controlled amounts of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, and silicon. This balance gives the material its signature strength and weldability, which are essential for high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
When you look at its mechanical properties, you’ll find that A105 carbon steel offers impressive tensile strength, yield strength, and hardness. These characteristics ensure that the flange can withstand significant stress without deforming or failing. The controlled manufacturing process guarantees that every kind of flange meets these minimum property requirements.
This combination of strength and resilience makes A105 an ideal material for flanges. Whether you’re dealing with a simple connection or a critical, high-stress joint, you can count on the predictable performance that comes from this standardized chemical composition and robust mechanical profile.
Common Applications in Piping Systems
You will find ASTM A105 flanges used extensively across many industries due to their versatility and strength. They are a fundamental component in building and maintaining robust pipelines. Their ability to handle pressure and temperature makes them suitable for a wide range of demanding services.
These pipe fittings are essential for creating secure, leak-proof connections between different parts of a piping system. You can use them to connect pipes to each other, attach pipes to valves, or join pipes to other important equipment like pumps and pressure vessels. This flexibility makes them indispensable in complex industrial setups.
Some of the most common applications include:
- Oil and gas processing and transportation pipelines
- Chemical and petrochemical plants
- Power generation facilities
- Water treatment and distribution systems
Slip-On A105 Flanges
A slip-on flange is one of the most common types of A105 pipe fittings. As its name suggests, this flange is designed to slide over the end of a pipe before being welded in place. Its inner diameter is slightly larger than the pipe’s outer diameter, allowing for easy positioning and alignment.
This kind of flange is typically secured with two fillet welds—one on the inside and one on the outside. Slip-on flanges are a cost-effective solution for low-pressure applications. They come in a wide class range and are defined by a clear specification for various uses. Let’s examine how to identify them and where they are best used.
Identifying Features and Typical Uses
How can you spot a slip-on flange? This kind of flange has a simple, flat design without a protruding neck or hub. The key identifying feature is that the inner diameter of the flange is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the pipe it’s meant for. This allows the pipe to slide right in. Once in position, you’ll notice a flat face with bolt holes around the perimeter for connection.
Slip-on flanges are preferred in systems where high pressure is not a concern. Their ease of installation and lower initial cost make them a practical choice for many general-purpose applications. They are especially useful in situations where precise pipe cutting is not required, as the flange’s position can be adjusted before welding.
You’ll typically find slip-on flanges used in:
- Low-pressure fluid pipelines
- Cooling water lines
- Fire protection systems
- Chemical processing lines with non-critical fluids
Installation Methods and Required Tools
The installation of a slip-on flange is a relatively straightforward process. First, you slide the flange over the end of the pipe and position it correctly. A small gap is typically left between the end of the pipe and the inner face of the flange to prevent any damage to the flange face during the welding process.
Once the flange is in place, it requires two fillet welds to secure it. One weld is applied to the outside where the hub meets the pipe, and a second weld is applied to the inside of the flange. This double-welding technique ensures a solid connection, though its strength is considered less than that of a weld neck flange.
For a successful installation, you will need the following tools and equipment:
- Welding machine and related safety gear
- Measuring tape for correct positioning
- Pipe fitter’s square or level for alignment
- Grinder for preparing weld surfaces
Weld Neck A105 Flanges
In contrast to the slip-on type, the weld neck flange is designed for high-stress applications. Also known as a high-hub or welding neck flange, this component features a distinctive tapered hub that transfers stress from the flange to the pipe itself. This design significantly reduces stress concentration at the bottom of the flange, providing a much stronger connection.
The manufacturing process for a weld neck flange involves forging the flange and hub as a single piece. The end of the neck flange is beveled to match the pipe’s wall thickness, allowing for a seamless butt weld. This creates a connection that is as strong as the pipe itself, making it ideal for demanding pipelines. Now, let’s explore its advantages and specifications.
Advantages Over Other Flange Types
The primary advantage of a weld neck flange lies in its superior structural integrity. The long, tapered hub provides significant reinforcement to the connection, making it suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, and sub-zero temperature applications. This design effectively handles bending moments and other stresses that would compromise other flange types.
Unlike a slip-on flange, a weld neck flange is connected to the pipe with a single, full-penetration butt weld. This welding method creates a smooth transition between the pipe and the flange, reducing turbulence and erosion inside the pipeline. The improved flow characteristics are a major benefit in many process systems.
Key advantages of the weld neck flange include:
- Excellent stress distribution, reducing fatigue
- High strength suitable for critical applications
- Superior performance under fluctuating pressure and temperature
- Enhanced durability due to its robust design and welding method
Size Range and Pressure Ratings Available
Weld neck A105 flanges are available in a comprehensive size range and various pressure ratings to meet diverse industry needs. The sizes are typically denoted by Nominal Pipe Size (NPS), ranging from small diameters like 1/2″ all the way up to 24″ and beyond for special applications. These sizes correspond to specific inner and outer diameters as defined by standards like ASME B16.5.
The pressure rating, often called the class range, indicates the maximum pressure the flange can withstand at a given temperature. These classes are expressed in pounds (lb), such as Class 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500. Higher class ratings mean the flange is thicker and can handle more pressure. Both ANSI and ASME standards provide detailed specifications for these ratings.
Here is an example of dimensions for a Class 150 weld neck flange:
NPS | Inside Diameter | Outside Diameter | Bolt Holes |
|---|---|---|---|
1″ | 1.05″ | 4.25″ | 4 |
2″ | 2.07″ | 6.00″ | 4 |
4″ | 4.03″ | 9.00″ | 8 |
6″ | 6.07″ | 11.00″ | 8 |
Additional A105 Flange Types
Beyond slip-on and weld neck flanges, the A105 family includes several other specialized types. For instance, a socket weld flange offers a similar installation concept to a slip-on but provides a better flow path. Another key type is the blind flange, which serves a completely different purpose by sealing off the end of a pipe or valve.
Many of these flanges are available with different face types, such as a raised face (RF), to ensure a proper gasket seal. These variations are designed to meet specific pressure requirements and connection needs, with standards like PN and BS providing further specifications for different markets. Let’s explore blind flanges and raised face variants in more detail.
Blind Flanges and Raised Face Variants
What is a blind flange? It’s essentially a solid disk with bolt holes used to close the end of a piping system or a valve opening. Unlike other flanges that connect pipes, a blind flange provides a secure and permanent seal. This makes it ideal for terminating a pipeline, performing pressure tests, or providing easy access for future expansion.
A raised face (RF) is a common feature you’ll find on many flange types, including blind flanges. The raised face is a small, elevated surface around the bore where the gasket sits. This design concentrates the pressure from the bolting force onto a smaller area, creating a more effective and reliable seal. The height of the raised face typically increases with the flange’s pressure class.
When choosing between flange faces, consider the following:
- Blind Flange: Used to cap or seal a pipe end.
- Raised Face (RF): Provides a concentrated sealing surface for a gasket.
- Ring Type Joint (RTJ): A grooved face for high-pressure sealing with a metal ring gasket.
- Flat Face (FF): Used in low-pressure applications, typically with cast iron fittings.
Comparing A105 to Alternative Materials
While A105 carbon steel is a fantastic all-around choice, certain applications may require alternative materials. The decision often depends on factors like corrosion resistance, temperature extremes, and the specific fluid being transported. ASTM standards cover a wide range of materials to meet these needs.
For environments with corrosive substances, stainless steel flanges (like ASTM A182 F304L or F316L) are a common alternative. Stainless steel offers excellent resistance to rust and chemical attack. For even more demanding conditions, high-nickel alloys like Inconel or Hastelloy provide superior performance at extreme temperatures and in highly corrosive media.
When comparing materials, think about:
- A105 Carbon Steel: Great strength and cost-effectiveness for general use.
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for corrosion resistance.
- Alloy Steels (e.g., F11, F22): Offer enhanced properties for high-temperature service.
- Nickel Alloys: Best for extreme temperature and corrosion challenges.
Benefits of Using Carbon Steel A105 Flanges
Why do so many industries rely on carbon steel A105 flanges? The primary benefits are their exceptional durability and cost-effectiveness. A105 carbon steel provides excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and toughness, ensuring that these flanges can withstand the rigors of industrial pipelines without fail.
This combination of performance and affordability makes A105 flanges a smart economic choice. You get a reliable, long-lasting component that meets stringent safety standards without the higher cost associated with stainless steel or other specialized alloys. Let’s break down these benefits further.
Durability and Cost-Effectiveness
The durability of A105 flanges starts with their manufacturing process. Most are produced through forging, a method that aligns the steel’s internal grain structure to enhance its strength and resistance to impact and fatigue. This process results in fittings that can endure high pressures and mechanical stress over long periods, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
From a financial perspective, A105 carbon steel offers significant cost-effectiveness. The raw materials are more abundant and less expensive to process than those for stainless steel or nickel alloys. This lower material cost, combined with an efficient manufacturing process, translates into a lower purchase price for you without sacrificing quality or performance for most standard applications.
Ultimately, choosing A105 flanges means you are investing in a product that provides a long service life at a reasonable cost. This balance of durability and affordability makes them one of the most popular choices for industrial pipe fittings worldwide.
Industry Standards and Specification Considerations
When selecting any flange, adhering to industry standards is non-negotiable. Standards from organizations like ASME, ANSI, and ASTM ensure that every flange is safe, reliable, and interchangeable. The ASTM A105 specification, for example, dictates the material’s chemical and mechanical properties, while ASME B16.5 defines the dimensions, tolerances, and pressure ratings.
Before making a purchase, you must confirm the correct specification for your application. This includes verifying the flange’s size (NPS), pressure class (e.g., Class 150 or 300), face type (RF, RTJ, etc.), and the required pipe schedule for weld neck flanges. Getting the specification right is crucial for ensuring a proper fit and a secure, leak-free connection.
Always check that your supplier provides flanges that are clearly marked with the required information, including the material grade (A105), manufacturer, size, class, and applicable standards. This traceability is your guarantee that the product meets the necessary quality and safety requirements for your project.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the various A105 flange types, including slip-on and weld neck flanges, is crucial for making informed decisions in piping systems. Each type has its unique features, advantages, and applications that can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of your projects. By considering the benefits of carbon steel A105 flanges, such as durability and cost-effectiveness, you can enhance your project’s success while adhering to industry standards. If you have any questions or need further assistance in selecting the right flanges for your needs, feel free to reach out for a consultation. Your project deserves the best components to ensure optimal performance!
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors should you consider when buying A105 flanges?
When purchasing A105 flanges, consider the required specification, including the size range (NPS), pressure class, and face type (e.g., RF, RTJ). Ensure the fittings comply with ANSI, ASME, and ASTM standards and are suitable for your application’s pressure and temperature. Always verify markings for traceability.
How do slip-on and weld neck flanges differ in application?
Slip-on and weld neck flanges differ mainly in their application strength. A slip-on flange is easier to install and ideal for low-pressure systems. A weld neck flange has superior mechanical properties due to its tapered hub and butt welding connection, making it the preferred choice for high-stress, high-pressure applications.
Are there any material alternatives to A105 for carbon steel flanges?
Yes, there are several material alternatives to A105 carbon steel. For enhanced corrosion resistance, stainless steel grades like F304L and F316L under the ASTM A182 standard are common. For high-temperature or highly corrosive environments, other alloy steels and nickel alloys like Inconel or Hastelloy are used.